Nail fungi (onychomycosis) in the foot is a disease that developed as a result of damage to nail plates with dermatophyte fungi (up to 96%), less often mold and yeast (about 4%).The infection is most commonly spread from the skin of the feet with long mycosis in the legs.Here you find favorable conditions for development - increased humidity and nutrients.Under the influence of the pathogens, the structure is disturbed and the color of the nail plates changes.Over time, their complete destruction occurs.
Onychomycosis is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a serious disease, which is subject to timely detection and adequate treatment under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Standing mushrooms are recorded in millions of people around the world.About 5% of the total population suffer from onycomycosis.The wider disease is common in humans 50 - 60 years.A person a second person is sick in this age group.Treatment of pathology is difficult for them due to the presence of somatic pathology, mainly vascular and endocrine.Men are sick more often than women.Older people get sick more often than young people.Children rarely suffer, mainly suffer from serious illness.With AIDS, the disease has an atypical appearance.
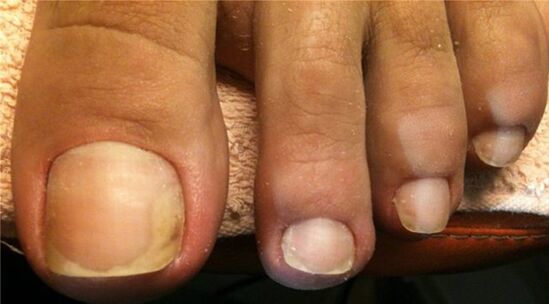
Causal agents of onycomycosis
The cause of onycomycosis in the foot is different types of fungi: dermatophytes, fungi similar to yeast or mold separately or in combinations.
- Dermatophytes and dermatophytes make up to 90% of all onycomycosis.They are represented by trichophyton fungi (most often T. rubrum and T.METAGROPHYtes VAR. Interdigital).Most often, the nail plates are affected by Trichophyton rubrum.Dermatophytes are common in places with a mild climate.
- Peak -like fungi of the genus Candida onhomycosis in the legs rarely cause.They make up about 3% of all onycomycosis.In addition to Candida Albicans, fungi such as S. tropicalis, S. Parapsylosis and S. Guiliermondii also cause disease.
- Most mold fungi are unable to cause nails on their own.Only some of their species are independent pathogens - these are scytalidium hyalinum and S. dimidiatum (Magniferee), which are not inferior to the pathogenicity of dermatophys.The foot onychomycosis is molds such as scopulariopsis brevacaulis, aspergillus s., Pyrenochaeta unguis-heominis, alternaria spp., Fusarium s.et al.Infection is more common in places with a hot and humid climate - tropics and subtropics.
The epidemiology of the disease
Most onycomycosis is anthropophilic infection.They are sick and spread mostly people infection.
Dermatophyte
The tank and source of dermatophy fungus is a sick person whose pathogens are transmitted through direct contact or his personal things.The infection almost always lies on the nails in the feet with the affected feet, whose disease continues both clearly and in secret (erased forms of mycosis).The risk of infection increases repeatedly in the presence of a disease in one of the family members.
The mushrooms are transmitted through shoes, clothes, files and nippers infected for nails, carpet, linen, towels, washing clothes, etc.The transmission of the infection occurs when the usual bath, in the shower, sauna, pool, gyms and on the beaches.Contributes to the entrance of the fungus to the foot while walking barefoot in the usual areas.Pathogens live for a long time on wooden floors and floors.
Peak -like mushrooms
Candida peak fungi are saprophytic flora and always live on a person's skin.A good immune system is contained in the growth of pathogens.Prolonged intake of antibiotics, contraceptives, glucocorticoids and cytostatics, endocrine pathology (often diabetes mellitus) and a number of diseases that exhaust the immune system.Explosive fungi penetrate the nails and mucous membranes of the patient himself, or enter the human body with infected carbohydrate -rich products.
Moldings
Molds live on land.Their disputes fall into environmental products, things and facilities.Nedimatophytes do not spread among people.
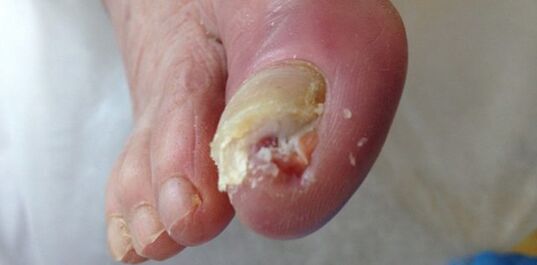
Risk factors for the development of the disease
For fungi, dermatophytes are characterized by an inherited predisposition, male sex, elderly, vascular disease, diabetes mellitus, immune conditions, increased sweating, nail damage and the presence of other dermatomycosis.
Candida yeast -like fungal infection is characterized by increased temperature and humidity, immune -condition, increased blood glucose, nail damage and non -compliance with personal hygiene rules.
For infection with mold fungi, severe immune conditions and nail damage are characteristic.
At risk
The risk group for the development of onykhomycosis includes:
- Persons who constantly use locker rooms, showers, saunas, etc.
- Professional athletes (swimmers, footballers, athletes, etc.).
- Military personnel and other groups of people using owner shoes.
- Male faces.
- Age is older than 60 years.
Contribute to the development of fungi in the legs:
- Wearing tight, tightly glued shoes.
- Increased sweating or dried legs.
- Nail injuries and erosion, legs, rooted nails, etc.
- Accommodation in wet and hot climate.
- Walking barefoot in public places.
- The presence of skin diseases in which keratinization of nails (psoriasis, ichthyosis) breaks down.
- Diseases such as diabetes mellitus, immune conditions, circulatory disorders of the lower extremities, blood disease, prolonged intake of corticosteroids, antibiotics and cytostatics.
- Genetic predisposition.
Flot fungal development paths
There are several ways to penetrate the mushrooms into the nail plate:
- Distal or distal-lateral (from free or lateral edge).
- Superficial (directly through the nail plate).
- Proximal (Subtyo -Gut).
The distal-lateral route of fungal penetration
The distal or distal pathway of penetration is characteristic of the trichophyton rubrum fungus.Pathogens are inserted into the nail plate from the free (distal) edge or lateral regions (side edge).The main inflammatory process occurs in the nail bed, where the expanded cell spread occurs.The bold layer of skin at the free edge thickens (hyperkeratosis), as a result of which the nail plate rises and exfoliates (onikolysis).
Further, the infection spreads to the hole and penetrates the nail plate, which is gradually (slowly) destroyed.With the damage to the matrix, total dystrophic onycomycosis occurs.
Hyperkeratosis of the nail bed is observed in chronic eczema, psoriasis, warts, flat red lichen.

The superficial way of the fungal spread
Trichophyton mushrooms Mentagophytes Var.Interdigital is more aggressive about the horny structures of nail plates than other dermatophytes.They mainly affect the outside of the nail plate, causing the development of white surface onycomycosis.The fungus under the influence of keratinas enzymes performs the layer of the hyphae layer, gradually capturing all layers of the nail plate.Mostly 1 and 5 fingers are affected.It is those who undergo the greatest trauma of shoes when walking.In the disease, 1 and 4 intercity folds are affected.
It is believed that the superficial form of onychomycosis can also be caused by fungi-non-hymanatophytes: acremonium spp., Fusarium oxysporum and some types of aspergillus.
Proximal fungal distribution route
There is a third path of fungi penetration into a nail plate - through a proximal nail roller and a nail bed.The loss begins with the skin in the nail roll area, which thickens and extracts from the surface of the nail.Further, the last part of the matrix and the nail bed is involved in the process, with the damage to which the furrows, irregularities and cracks in the nail appear.With the penetration of pathogens into the nail plate, the nail acquires a dark white color over time.Over time, there is complete destruction and loss of nail plate.Most often found in HIV -infected patients with the spread of infection through blood vessels.
Characteristics of fungi damage similar to the peaks of the genus Candida
Damage to the genus Candida begins with a paronichia - inflammation of the proximal roller (located near the hole).Its edema and thickening are observed, which leads to the separation of the cuticle from the surface of the plate.Further, the fungus falls freely into the matrix and the nail bed, causing, causing the nail from the finger tissue over time.
Characteristics of fungal damage from incorpoons
Nail damage to the fungus with no -the heart is secondary.Molds (often scytalidium spp.) Is placed on already affected nails - cracks, space between nail bed scaffolds or desert vessels.Next, hyperkeratosis develops and slow destruction of the nail plate.
Clinical forms of onycomycosis in the foot
There are several forms of onycomycosis in the legs:
- Distal-lateral.
- Surface white.
- Proximal.
- Total dystrophic.
Onycomycosis of the distal-lateral submarine in the foot
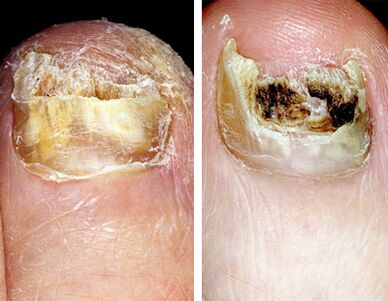
This form of the disease is more common.In most cases, the cause of onycomycosis is dermatomycetes, in particular trichophyton rubrum.The pathogens penetrate the nail plate from the free edge and the side edges.Perenophaeum hyperkeratosis develops, as a result of which there is a nail detachment from the finger tissue (onycholysis), it loses transparency, acquires a white or yellow color, begins to be destroyed.With the development of submarine hyperkeratosis, the nail plate looks thick.With the progression of the disease, the concentration of the lesion expands towards the hole, as shown by the developing yellow straps.Over time, the entire nail plate and matrix are included in the pathological process, which over time leads to dystrophy and destruction of the nail.
In older people, pronounced hyperkeratosis (obesity), onychogrifosis (obesity and deformation in the form of bird claws) or coilonichia (concave deformation) is often observed.Their nails are often affected by mixed flora - dermatophytes, mold and even bacteria.
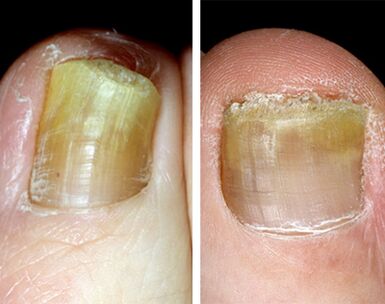
The superficial (white) form of onycomycosis in the foot
The onycomycosis of the white surface in the foot is the second largest form of damage distribution.Its cause is mainly Trichophyton Mentagophytes Var.Interdigital, which penetrates the nail plate directly through its upper (pre-RSAL), as well as some types of fungi-jo-hectites.Mostly affected by the nail on the front of the foot, less often - the fifth.
At first, small white dots and strips appear on their surface, which eventually amazes a growing surface.Gradually, the color becomes yellow, ocher.The nail surface becomes loose, rough, powder, lightly poured.Obesity and separation from the nail bed do not occur.
Submarine proximal form of onychomycosis in the foot
This form of mycosis is a rarity.It makes up about 3% of all onycomycosis.The reason is the peak -like fungi of Candida Albicans and Trichophyton rubrum.Nail candidiasis is preceded by inflammation of the periological roll.Bow, wins red, becomes great.The cuticle is raised and the infection penetrates the last part of the matrix and the nail bed, when damaged by the furrows, irregularities and cracks in the nail plate, the loss of natural and clouding loss is marked.Gradually, the nail is destroyed, in severe cases disappears.This form of onycomycosis in the legs is often found in HIV -infected patients.
Total dystrophic form of onycomycosis in the foot
This form of onychomycosis most often develops with a long -term current disease (chronic course), the cause of which are most often the fungus of the Trichophyton rubrum and Candida albicans.At the same time, nail plate, bed and matrix are included in the pathological process.Spending the nail occurs as a result of the development of submarine hyperkeratosis.Over time, the nail plate is destroyed, and the new due to the affected matrix does not grow or grow poorly.
Types of nail plate damage
There are 3 options for onychomycosis:
- Normotorophical.
- Hypertrophic.
- Atrophic.
Normotrophic type of onycomycosis in the foot
With a type of normotrophic, the infection is located in the upper layers of the nail plate.Its thickness and color in the disease do not change, but stains and stripes are visible in depth.The nail color varies from white to saturated yellow.After some time, the points and straps come together.The damage area spreads throughout the nail plate, excluding the moon.Fracture and peeling is not observed.Sometimes a slight release of the free edge is marked.With adequate treatment, a cure is possible.
Hypertrophic type of onycomycosis in the foot
This type of onychomycosis is the most common.As a result of the development of submarine hyperkeratosis, the nail plate is significantly thickened, deformed and loses its brightness.The nails become uneven, dull, acquire a brown-gray color and crumble.The moon area is not affected.The disease gives the patient vulnerable discomfort.In elderly patients, the development of onychogrifosis is marked - nails thicken, lengthen and bend like the claws of a bird.
Atrophic type of onycomycosis in the foot
With a type of atrophic (onycolitical), the nail plate quickly loses its connection from the nail bed, many gaps appear in its layers, fades, becomes thinner and changes color to white or white yellow.The surface remains smooth for a long time.Over time, partial destruction occurs.
Signs and symptoms of nail fungus
Most often, the change in the nail begins with a free (distal) or lateral (lateral) edge.
Color change.With onychomycosis, a change in the color of the nail plate is the first sign of the disease.It becomes dark, often loses its brightness, acquires a white or yellow color, with overlapping with mold mushrooms - brown, brown, green and even black.
Obesity.Increasing the number of horny masses as a result of the development of submarine hyperkeratosis leads to nail thickening.
Oppression and destruction.In the event of the disease as a result of the vital activity of the fungus, the nail plate is first destroyed and further, over time, was completely destroyed.

Characteristics of nail damage with different types of onycomycosis
Nail damage with different types of fungal diseases has its own characteristics.The main types of pathogens are Trichophyton rubrum (70 - 90%) and Trichophyton Mentagophytes v.interdigital (8 - 30%).Candida albicans, mold fungi, T. Mentagophytes v.Gypsum, T. Verrucosum, T. Tonsuras and T. violaceum, floccosum epidermophyton, trichophyton are much less common.Schonleinii.
Onyikomycosis in the foot with rubofitia
Rubrofitics in the Russian Federation accounts for 70 to 90% of all mycosis.The legs in the disease are most often affected (usually a type of dry squamosis).An indispensable satellite of the foot rubofit is a nail fungus.With mycosis, the distal-dyilutal form of onycomycosis usually develops, pronounced hyperkeratosis is characteristic, some fingers on the foot are touched once and often the fingers on one side.The disease continues without particular subjective sensations.Pain and discomfort when wearing shoes occurs with pronounced hyperkeratosis, onichogrifosis and a clumsy nail.The source of infection is often in the patient's family.
Often, associated onycomycosis is recorded: Trichophyton rubrum and Candida albicans, trichophyton rubrum and mold.It is important to evaluate the cultural study.
Onikomycosis in the legs with t.Mentagrophytes fungus.V.INTERDIGITAL
Mushrooms T. MentaGrofites.V. interdigital affects the skin of the feet and nails.Epidermofytosis accounts for 10 to 30% of all my friend.
With the disease, the upper part of the nail plate is affected.The surface white form of onycomycosis usually develops.The pathological process is mainly involved in 1 and 5 fingers (they are subject to greater trauma from shoes while walking) and 1 and 4 inter -casket folds.Transmission of infection occurs when using an ordinary bath, in the shower, sauna, pool, on beaches and pools.
Onycomycosis in the legs with damage to fungi -like peaks of the genus Candida
This form of mycosis in the leg is a rarity.It accounts for less than 3% of all onycomycosis.Often the disease is recorded in people with chronic generalized candidiasis.Nail damage, as a rule, begins with the inflammation of the periology roll near the hole.Its edema and thickening are observed, which leads to the separation of the cuticle from the surface of the plate.Further, the fungus falls freely on the matrix and the nail bed (proximal and subibble shape), if grooves, irregularities and cracks appear, a loss of natural and clouding appears, a brown-brown color appears.Gradually, the nail is destroyed, in severe cases disappears.

Onycomycosis in the legs caused by molds
Plastic mushrooms are populated on a nail already affected, in the spaces between the nail bed scaffolds or desert boats.Next, hyperkeratosis develops and slow destruction of the nail plate, which during the disease is stained in black (scytalidium spp.) Or green or gray (scopulariopsis brevicaulis) color.
Diagnosis of onycomycosis
The diagnosis of onychomycosis is based on data from epidemiological history, the clinical appearance of the disease and the data of the laboratory research method.
In a microscopic examination of the material, the nature of the disease (fungus or other pathogen) is established.The identification of the fungus is created with a microbiological examination (the crops of the material in a nourishing medium) with the subsequent microscopy of a clean crop.The process is laborious, success is achieved in half of the cases.Accurate collection of material from affected nails is the key to a successful microbiological study.
Diagnosis
Only in half of the cases of patients with dermatologists with changes in the shape and color of the nails make fungal diseases.Onychomycosis should be distinguished from eczema, psoriasis, Reitera syndrome, pachionichia, Daria disease, flat liqueur, Norwegian scabies, bacterial lesions.